
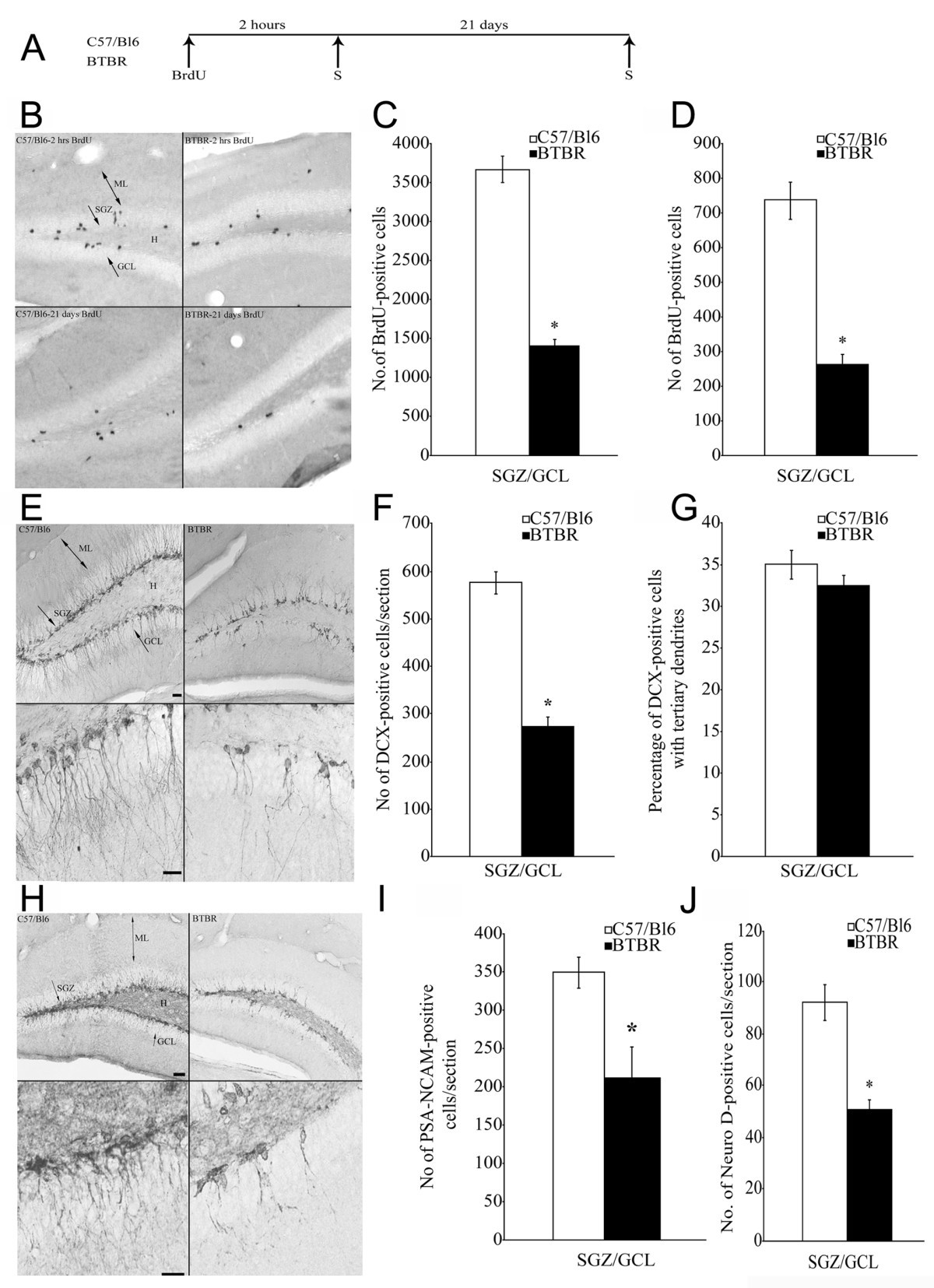
Our aim was to compare cerebellum-dependent delay eyeblink classical conditioning and hippocampus-dependent contextual fear conditioning in the same animals using the same conditioned and unconditioned stimuli for eyeblink and fear conditioning. We examined learning over the adult life span in CBA mice, along with morphological and electrophysiological substrates.

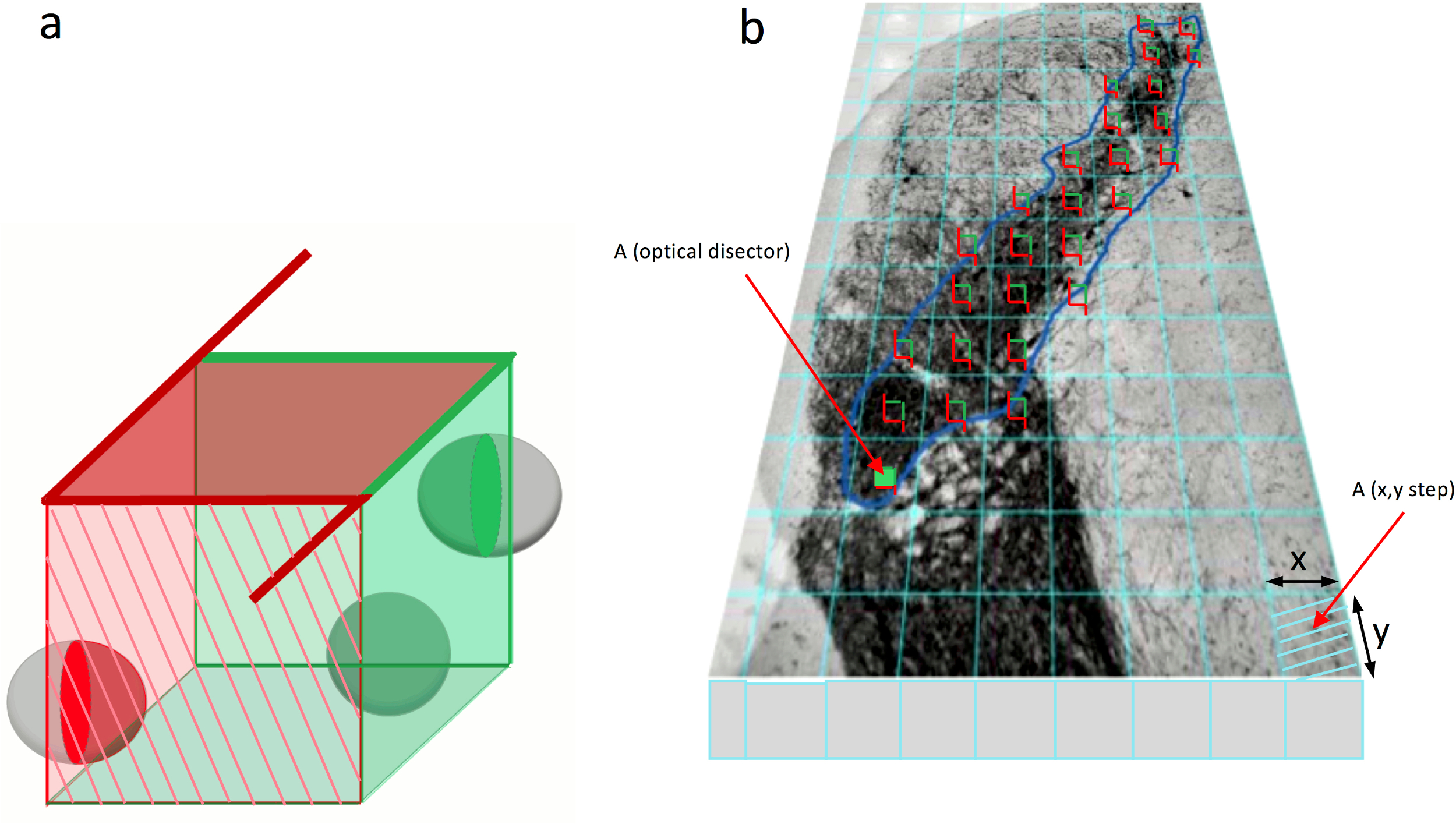
364, 6–15 (1996).Cognitive functions show many alternative outcomes and great individual variation during normal aging. Methods for determining numbers of cells and synapses: a case for more uniform standards for review. New sterological methods for counting neurons. The new stereological tools: disector, fractionator, nucleator and point sampled intercepts and their use in pathological research and diagnosis. Early rearing environment and dorsal hippocampal ibotenic acid lesions: long-term influences on spatial learning and alternation in the rat. The effects of dietary fatty acid composition combined with environmental enrichment on brain and behavior in mice. In vivo growth factor expansion of endogenous subependymal neural precursor cell populations in the adult mouse brain. FGF-2-responsive neuronal progenitors reside in proliferative and quiescent regions of the adult rodent brain. A multipotent EGF-responsive striatal embryonic progenitor cell produces neurons and astrocytes. Gonadal and adrenal steroids regulate neurochemical and structural plasticity of the hippocampus via cellular mechanisms involving NMDA receptors. Regulation of adult neurogenesis by excitatory input and NMDA receptor activation in the dentate gyrus. The genetic organization of neuron number in the granule cell layer of the area dentata in house mice. Changes in hippocampal neuronal nuclei in response to environmental stimulation. Calcium-binding protein (calbindin-D28k) and parvalbumin immunocytochemistry: localization in the rat hippocampus with specific reference to the selective vulnerability of hippocampal neurons to seizure activity. Immunocytochemical detection of 5′-bromodeoxyuridine incorporation in the central nervous system of the mouse. A developmental theory of environmental enrichment. Environmental complexity modulates growth of granule cell dendrites in developing but not adult hippocampus of rats. The effects of environmental complexity on the histology of the rat hippocampus. Environmental complexity, cerebral change, and behavior. Social grouping cannot account for cerebral effects of enriched environments. Effect of neonatal handling on age-related impairments associated with the hippocampus. Experiential modificaiton of the developing brain. Environmentally induced changes in the brains of elderly rats.
Autoradiographic examination of the effects of enriched environment on the rate of glial multiplication in the adult rat brain.
Effects of environmental complexity and training on brain chemistry and anatomy. Neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of the adult rat: age-related decrease of neuronal progenitor proliferation. Differentiation of newly born neurons and glia in the dentate gyrus of the adult rat. Neurogenesis in the adult rat: electron microscopic analysis of light radioautographs. Autoradiographic and histologic evidence of postnatal neurogenesis in rats.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
